GAP Bluetooth Low Energy: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Advertising Process == | == Advertising Process == | ||
The following illustration should explain the advertising process and how the advertising payloads and scan response payloads work. | |||
A peripheral will set a specific advertising interval, and every time this interval passes, it will retransmit it's main advertising packet. A longer delays saves power but feels less responsive if the device only advertises itself once every 2 seconds instead of every 20ms. | |||
If a listening device is interested in the scan response payload (and it is available on the peripheral) it can optionally request the scan response payload, and the peripheral will respond with the additional data. | |||
[[File:gap_adv.png]] | |||
== Broadcast Network Topology == | == Broadcast Network Topology == | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 14 December 2017
GAP
GAP is an acronym for the Generic Access Profile, and it controls connections and advertising in Bluetooth. GAP is what makes your device visible to the outside world, and determines how two devices can (or can't) interact with each other.
Device Roles
GAP defines various roles for devices, but the two key concepts to keep in mind are Central devices and Peripheral devices.
- Peripheral devices are small, low power, resource contrained devices that can connect to a much more powerful central device. Peripheral devices are things like a heart rate monitor, a BLE enabled proximity tag, etc.
- Central devices are usually the mobile phone or tablet that you connect to with far more processing power and memory.
Advertising and Scan Response Data
There are two ways to send advertising out with GAP. The Advertising Data payload and the Scan Response payload.
Both payloads are identical and can contain up to 31 bytes of data, but only the advertising data payload is mandatory, since this is the payload that will be constantly transmitted out from the device to let central devices in range know that it exists. The scan response payload is an optional secondary payload that central devices can request, and allows device designers to fit a bit more information in the advertising payload such a strings for a device name, etc.
Advertising Process
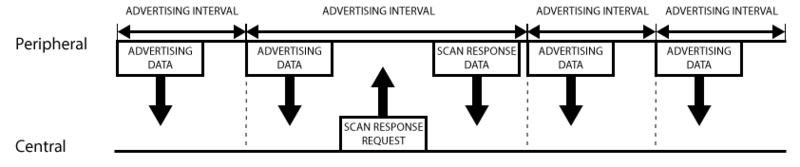
The following illustration should explain the advertising process and how the advertising payloads and scan response payloads work.
A peripheral will set a specific advertising interval, and every time this interval passes, it will retransmit it's main advertising packet. A longer delays saves power but feels less responsive if the device only advertises itself once every 2 seconds instead of every 20ms.
If a listening device is interested in the scan response payload (and it is available on the peripheral) it can optionally request the scan response payload, and the peripheral will respond with the additional data.