Install DNS in raspberry pi: Difference between revisions
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
=====DNS Package Installation===== | =====DNS Package Installation===== | ||
we use bind9 package for our DNS server and dnsutils for troubleshooting tool | we use bind9 package for our DNS server and dnsutils for troubleshooting tool | ||
* sudo apt install bind9 dnsutils | * <b>sudo apt install bind9 dnsutils</b> | ||
=====DNS File Configuration===== | =====DNS File Configuration===== | ||
After we installed the packaged in our DNS server, we will get the configuration folder in /etc/bind/ | After we installed the packaged in our DNS server, we will get the configuration folder in /etc/bind/ | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
* /etc/bind/named.conf.default-zones: default zones such as localhost, its reverse, and the root hints | * /etc/bind/named.conf.default-zones: default zones such as localhost, its reverse, and the root hints | ||
First of all we have to configure our zones so we have domain zone and IP zone (forward zone and reverse zone) | First of all we have to configure our zones so we have domain zone and IP zone (forward zone and reverse zone) | ||
* Sudo nano /etc/bind/named.conf.local | * <b>Sudo nano /etc/bind/named.conf.local</b> | ||
then we add the configuration of both zones into file | then we add the configuration of both zones into file | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
Forward zone: db.infosec.com | Forward zone: db.infosec.com | ||
<pre> The configuration template have been made similar to the db.local so we can copy that file to be our file (db.infosec.com) and db.192 is the same structure too.</pre> | <pre> The configuration template have been made similar to the db.local so we can copy that file to be our file (db.infosec.com) and db.192 is the same structure too.</pre> | ||
* Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.local /etc/bind/db.infosec.com | * <b>Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.local /etc/bind/db.infosec.com </b> | ||
* Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.infosec.com | * <b> Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.infosec.com</b> | ||
<div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | <div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | ||
; BIND data file for local loopback interface | ; BIND data file for local loopback interface | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
* Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.infosec.com /etc/bind/db.192 | * <b> Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.infosec.com /etc/bind/db.192 </b> | ||
* Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.192 | * <b> Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.192 </b> | ||
<div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | <div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
To configure the network interface as we use version 20.0 so it is configured by netplan. | To configure the network interface as we use version 20.0 so it is configured by netplan. | ||
* Sudo nano /etc/netplan/file_name | * <b> Sudo nano /etc/netplan/file_name </b> | ||
File_name it is already created so we can go to that location we will get it. The apply this configuration | File_name it is already created so we can go to that location we will get it. The apply this configuration | ||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
Then we have to write this command to apply the configuration | Then we have to write this command to apply the configuration | ||
* Sudo netplan apply | * <b>Sudo netplan apply </b> | ||
Finally, we have to configure resolv.conf | Finally, we have to configure resolv.conf | ||
* Sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf | * <b>Sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf</b> | ||
<div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | <div style="border : 2px solid gray "> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 19 November 2021
Local DNS Installation Procedure Using Raspberry Pi
Requirement and Devices
- Devices check-list
- Two Raspberry Pi (server, client) + 16GB SD Card
- Networking devices: switch, network Cable, Router , Keyboard and Mouse.
- Technology
- Raspberry Pi Ubuntu Server Operating System
- Reference: https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Raspberry Pi Imager
- Reference: https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/
- Putty for remote ssh to our Raspberry Pi
- Reference: https://www.putty.org/
- Raspberry Pi Ubuntu Server Operating System
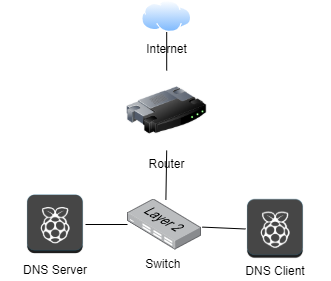
- System Physical Architecture
Installation Process
We assume that:
- Both Raspberry Pi have been installed ubuntu server operating system
- Our local network has been connected to internet and local network with LAN: 192.168.0.1/24 (gateway: 192.168.0.1)
DNS Server:
- Hostname: server.inforsec.com
- IP address: 192.168.0.2
DNS Client:
- Hostname: client.infosec.com
- IP address: 192.168.0.3
DNS Package Installation
we use bind9 package for our DNS server and dnsutils for troubleshooting tool
- sudo apt install bind9 dnsutils
DNS File Configuration
After we installed the packaged in our DNS server, we will get the configuration folder in /etc/bind/
- /etc/bind/named.conf.options: global DNS options
- /etc/bind/named.conf.local: for your zones
- /etc/bind/named.conf.default-zones: default zones such as localhost, its reverse, and the root hints
First of all we have to configure our zones so we have domain zone and IP zone (forward zone and reverse zone)
- Sudo nano /etc/bind/named.conf.local
then we add the configuration of both zones into file
Note:for indenting we can’t use tab button, we have to use space button
Forward zone and Reverse zone:
zone "infosec.com" IN {
type master;
file "/etc/bind/db.infosec.com";
}; //db.infosec.com it is just the name so we can put anything we want
zone "0.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "/etc/bind/db.192";
}; //the same case that db.192 it is just the name so we can but anything we want
Secondly, we have to configure file of each zones (forward and reverse zone) Forward zone: db.infosec.com
The configuration template have been made similar to the db.local so we can copy that file to be our file (db.infosec.com) and db.192 is the same structure too.
- Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.local /etc/bind/db.infosec.com
- Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.infosec.com
- BIND data file for local loopback interface
-
- $TTL 604800
- @ IN SOA server.infosec.com. root.server.infosec.com. (
2 ; Serial
604800 ; Refresh
86400 ; Retry
2419200 ; Expire
604800 ) ; Negative Cache TTL
- @ IN NS server.infosec.com.
- @ IN A 192.168.0.2
- server IN A 192.168.0.2
- host IN A 192.168.0.2
- client IN A 192.168.0.3
- client1 IN A 192.168.0.3
- server and host is the name that we set for machine 192.168.0.2 (DNS Server)
- client and client1 are the name that we set for machine 192.168.0.3
- Sudo cp /etc/bind/db.infosec.com /etc/bind/db.192
- Sudo nano /etc/bind/db.192
- BIND data file for local loopback interface
- $TTL 604800
- @ IN SOA server.infosec.com. root.server.infosec.com. (
2 ; Serial
604800 ; Refresh
86400 ; Retry
2419200 ; Expire
604800 ) ; Negative Cache TTL
-
- @ IN NS server.infosec.com.
- @ IN PTR infosec.com
- server IN A 192.168.0.2
- host IN A 192.168.0.2
- client IN A 192.168.0.3
- client1 IN A 192.168.0.3
- 2 IN PTR server.infosec.com
- 3 IN PTR client.infosec.com
Thirdly, we have to configure our network address and resolv.conf file
To configure the network interface as we use version 20.0 so it is configured by netplan.
- Sudo nano /etc/netplan/file_name
File_name it is already created so we can go to that location we will get it. The apply this configuration
network:
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.0.2/24]
gateway4: 192.168.0.1
nameservers:
search: [infosec.com]
addresses: [192.168.0.2]
Then we have to write this command to apply the configuration
- Sudo netplan apply
Finally, we have to configure resolv.conf
- Sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf
Nameserver 192.168.0.2 Search infosec.com
For client side we use configure network address like the interface above but with different IP address and set resolv.conf the same as DNS server.
Testing
To test if our configuration is correct or not, we can use ping and nslookup.
- If you use ping it will respond, even you use IP or name of server.
PING 192.168.0.2 (192.168.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.104 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.093 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.069 ms
- Using ping with name
PING server.reatrey.com (192.168.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from server.reatrey.com (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.060 ms
64 bytes from server.reatrey.com (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.083 ms
64 bytes from server.reatrey.com (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.070 ms